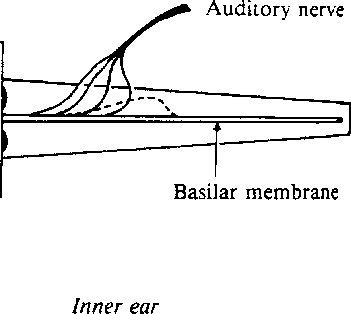
The cochlea transforms pressure variations into properly coded
neural impulses.
As a first approximation, consider an unraveled cochlea and only
two main sections separated by the basilar membrane:
- the scala tympani (bottom)
- the scala vestibule (top)
The oval and round windows are at the larger end of the
cylinder, and a small hole (helicotrema) is at the smaller end to
connect the two sections.
``Music 175: Ear Physiology''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (ear175.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (ear175.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (ear175_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (ear175_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-04-09 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>