The decibel (dB) is a unit
named after Alexander Graham Bell, known as a telecommunications pioneer.
A decibel is defined as one tenth of a bel, i.e., to convert
from Bel to dB you multiply by 10:
The decibel is a logarithmic scale, used to compare two
quantities such as the power gain of an amplifier
or the relative power of two sound sources.
The decibel difference
between two power levels 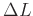 for example, is defined in terms
of their power ratio
for example, is defined in terms
of their power ratio 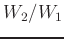 and is given in decibels by:
and is given in decibels by:
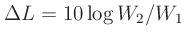
dB
Since power is proportional to intensity, the ratio of two
signals with intensities 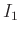 and
and 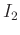 is similarly given in
decibels by
is similarly given in
decibels by
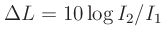
dB
``Music 270a: Fundamentals of Audio, Acoustics and Sound''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (funAudio.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (funAudio.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (funAudio_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (funAudio_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-09-30 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>