Classic amplitude modulation (AM) is more general.
Modulating signal includes a constant (DC offset):
(where the first term is the modulating signal.)
DC component 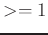 makes the modulating signal
unipolar, i.e., the entire signal is greater than zero.
makes the modulating signal
unipolar, i.e., the entire signal is greater than zero.
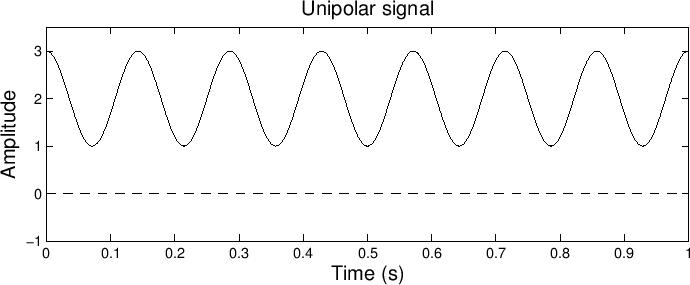
Figure 6:
A unipolar signal.
|
 |
``Music 171: Amplitude Modulation''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (am171.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (am171.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (am171_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (am171_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-11-05 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>
![]()
![]() makes the modulating signal
unipolar, i.e., the entire signal is greater than zero.
makes the modulating signal
unipolar, i.e., the entire signal is greater than zero.