- A ``real-world'' signal is captured using a microphone which has a diaphragm
that is pushed back and forth according to the compression and rarefaction of the sounding pressure waveform.
- The microphone transforms this displacement into a time-varying
voltage--an analog (continuous-time) electrical signal.
- The process by which an analog signal is digitized is called
analog-to-digital or ``a-to-d'' conversion
- conversion is done using hardware called an
analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
- In order to properly represent the electrical signal within the
computer, the ADC must accomplish two tasks:
- sampling: digitize the time variable
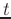 ;
;
- quantization: digitize the instantaneous
amplitude of the pressure variable
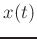 .
.
``Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (digitalAudio.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (digitalAudio.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (digitalAudio_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (digitalAudio_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-09-30 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>