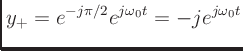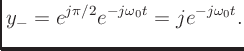The real sinusoid
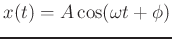 can be converted to
an analytic signal, by generating a phase quadrature
component,
can be converted to
an analytic signal, by generating a phase quadrature
component,
to serve as the imaginary part.
- Consider the positive and negative frequency components of a
real sinusoid at frequency
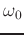 :
:
- Apply a phase shift of
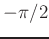 radians to the
positive-frequency component,
radians to the
positive-frequency component,
and a phase shift of 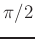 to the negative-frequency component,
to the negative-frequency component,
- Form a new complex signal by adding them together:
``Music 270a: Complex Exponentials and Spectrum Representation''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (compExpAndSpecRep.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (compExpAndSpecRep.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (compExpAndSpecRep_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (compExpAndSpecRep_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-10-21 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>
![]() can be converted to
an analytic signal, by generating a phase quadrature
component,
can be converted to
an analytic signal, by generating a phase quadrature
component,