Sampling is carried out by the change of variables
where 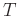 is the temporal sampling interval, and
is the temporal sampling interval, and
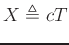 ,
is the spatial sampling interval
,
is the spatial sampling interval
Substituting into the traveling-wave solution yields
Since 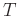 multiplies all arguments it is typically suppressed.
multiplies all arguments it is typically suppressed.
This notation is also used to model pressure in acoustic tubes.
``Music 206: Digital Waveguides''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (dwg.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (dwg.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (dwg_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (dwg_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-05-01 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>
![]() multiplies all arguments it is typically suppressed.
multiplies all arguments it is typically suppressed.