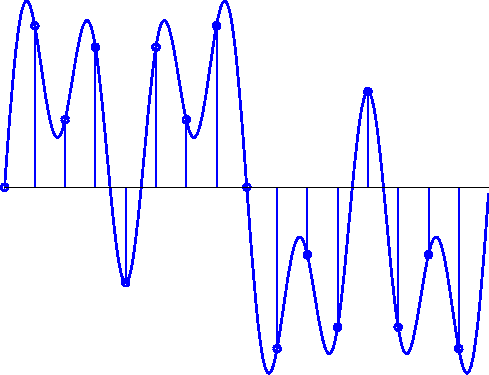
When analog signals are brought into a computer, they must be
made discrete (finite and countable).
A discrete-time signal is a finite sequence of
numbers, with finite possible values for each number.
- number values are limited by how many bits are used to
represent them (bit depth);
- can be stored on a digital storage medium.
Sampling: the process of taking individual values of a
continuous-time signal (at regular time intervals).
``Music 171: Fundamentals of Digital Audio''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (digitalAudio171.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (digitalAudio171.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (digitalAudio171_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (digitalAudio171_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-10-15 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>