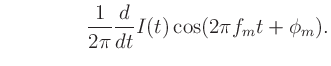The function 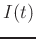 , called the
modulation index envelope, determines significantly the
harmonic content of the sound.
, called the
modulation index envelope, determines significantly the
harmonic content of the sound.
Given the general FM equation
the instantaneous frequency 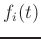 (in Hz) is given by
(in Hz) is given by
``Music 270a: Modulation''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (modulation.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (modulation.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (modulation_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (modulation_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-10-28 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>
![]() , called the
modulation index envelope, determines significantly the
harmonic content of the sound.
, called the
modulation index envelope, determines significantly the
harmonic content of the sound.
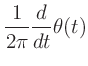
![$\displaystyle \frac{1}{2\pi}\frac{d}{dt}\left[2\pi f_ct + I(t)\cos(2\pi f_mt + \phi_m) + \phi_c\right]$](img63.png)
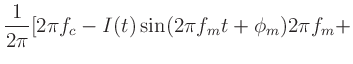
![$\displaystyle \qquad \qquad \frac{d}{dt}I(t)\cos(2\pi f_m t + \phi_m)]$](img65.png)