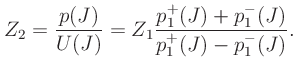A change in tube cross-sectional area creates a
junction between two impedances 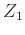 and
and 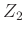 .
.
Figure 5:
Tube with a change in cross-sectional area.
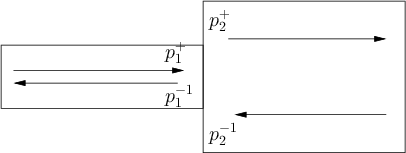 |
The pressure and velocity at the junction
is given by
where
The new impedance at the junction 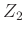 , is given by
, is given by
``MUS 206: Modeling Acoustic Tubes and Wind Instrument Bores/Bells''
by Tamara Smyth,
Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Download PDF version (wind.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript version (wind.ps.gz)
Download PDF `4 up' version (wind_4up.pdf)
Download compressed PostScript `4 up' version (wind_4up.ps.gz)
Copyright © 2019-05-22 by Tamara Smyth.
Please email errata, comments, and suggestions to Tamara Smyth<trsmyth@ucsd.edu>
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
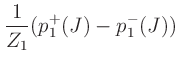
![]() , is given by
, is given by